Table of Contents
How Long Does a Car Battery Last? The General Question
Car ownership comes with its share of questions, and one of the most common ones is, “How long does a car battery last?” This question is not just about the lifespan of a car battery but also touches on the importance of maintenance, the impact of usage patterns, and how to maximize the life of your battery. Let’s delve into the intricacies of car battery life and uncover some essential tips to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Factors Influencing Car Battery Life
Several factors can affect how long a car battery lasts, including climate, driving habits, and the electrical demands of your car. Typically, a car battery can last between 3 to 5 years, but this can vary widely based on these conditions.
Climate
Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can significantly shorten a battery’s lifespan. Heat accelerates corrosion inside the battery, while cold increases the electrical resistance and thickens engine oil, making it harder for your battery to perform.
Driving Habits
Short trips don’t allow the battery to fully charge, leading to a condition called sulfation which can decrease the battery’s lifespan. On the other hand, regular, longer trips help keep the battery fully charged and in good health.
Electrical Demands
Modern vehicles come packed with electronics that can strain the battery, especially if used when the engine isn’t running. Ensuring that your battery can meet these demands is crucial for its longevity.
How Long to Charge a Car Battery
Understanding how long to charge a car battery is essential for maintaining its health and longevity. A typical charge can take about 4 to 24 hours, depending on the battery’s state and the charger’s output. Regularly charging your battery can help maintain its capacity and prevent unexpected failures.
Maximizing Battery Life
To extend the life of your car battery, consider the following tips:
- Regularly check the battery’s terminals and connections for corrosion and clean them as needed.
- Keep the battery tightly fastened to minimize vibration damage.
- Use a battery maintainer if you plan not to use your car for extended periods.
- Ensure your car’s electrical system is regularly checked by a professional.
In conclusion, asking “How long does a car battery last?” reveals the need for awareness about battery maintenance and the factors that affect its lifespan. By understanding these elements and taking proactive steps, you can ensure your car’s battery serves you well for as long as possible. Remember, a little care goes a long way in extending the life of your car’s battery.
Incorporating these insights into your vehicle maintenance routine can significantly influence the longevity and reliability of your car battery, making every journey smoother and worry-free.

Most Searched 11 Key Questions about Car Battery Lifespan are Answered
FAQ 1- How Long Does a Car Battery Last After Being Charged?
The duration a car battery lasts after being fully charged depends on several factors including the battery’s age, its condition, the type of vehicle, and how the vehicle is used. Here’s a general breakdown to give you an idea:
- Battery Age and Condition: A new, healthy car battery can keep its charge for about two weeks to two months without being driven. However, as a battery ages, its ability to hold a charge diminishes. A battery older than 3-5 years may struggle to maintain a charge for long periods.
- Vehicle Type: Vehicles with higher electrical demands (due to advanced electronic systems, for example) may drain a battery faster.
- Climate and Storage: Extreme temperatures (both hot and cold) can significantly affect battery performance. Batteries tend to discharge quicker in cold weather. If the vehicle is stored in a garage and away from extreme temperatures, the battery will last longer after being charged.
- Driving Habits: Regularly driving your vehicle allows the alternator to recharge the battery. If you only make short trips, the battery may not fully recharge, reducing how long it lasts after being charged.
FAQ 2- How Long Does a Car Battery Last After Being Jumped?
After being jump-started, the duration a car battery will last depends largely on the reason it needed a jump in the first place and the condition of the battery. Here are some factors to consider:
- Battery Age and Condition: If the battery is relatively new and in good condition, but was discharged due to leaving the lights on or a similar one-time drain, it might recover fully after being jump-started and can last for its normal lifespan (3-5 years on average). However, if the battery is old or in poor condition, it may not hold a charge for long and could require replacement soon after.
- Driving Duration Post-Jump: Immediately after a jump-start, driving the vehicle for at least 20-30 minutes without turning it off can help recharge the battery. If the alternator and charging system are functioning correctly, this may be enough to restore the battery to a state where it can start the car on its own for a while. However, this doesn’t guarantee long-term battery health.
- Underlying Issues: If the need for a jump-start was due to an underlying issue like a faulty alternator, parasitic drain, or chronic battery undercharging, the battery may not last long after the jump if these issues aren’t addressed.
- Repeated Jump-Starts: Needing multiple jump-starts in a short period is a strong indicator of a failing battery or other electrical system problems. In such cases, the battery’s lifespan after each jump-start can drastically reduce.
In general, if a battery is jump-started due to a one-off discharge and is otherwise healthy, it can continue to operate effectively for its expected lifespan. However, if jump-starts become frequent or the battery is old, it may only last a few days to weeks after being jump-started, and replacement will likely be necessary. It’s crucial to get the battery and charging system checked by a professional after a jump-start to diagnose any potential issues.
FAQ 3- How Long Does a Car Battery Last with Lights on?
To estimate how long a car battery would last with the headlights and other interior lighting on, let’s consider the following factors:
- Battery Capacity: The average car battery has a capacity of about 48 amp-hours (Ah).
- Headlight Consumption: Modern headlights, especially if they are LED, consume about 55 watts (W) per unit. So, for two headlights, that’s 110W total. Assuming a car system voltage of 12 volts (V), the current draw would be,
- I (Current) = P (Power) [÷] V (Volts) I= 110W÷12V ≈ 9.17 amps
- Interior Lighting Consumption: Let’s assume interior lighting consumes about 20W total (which may vary greatly depending on the vehicle and the number of lights on). This would be an additional,
- I=20W÷12V ≈ 1.67 amps
- Total Consumption: Adding both values, we get a total consumption of 9.17+1.67=10.84A
Now, to find out how long the battery would last, we use the formula:
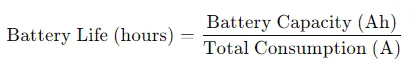
Let’s calculate this with the given values.
With the headlights and interior lighting on, drawing a total of approximately 10.84 amps, an average car battery with a capacity of 48 amp-hours would last about 4.43 hours which is around 4 hours and 25 minutes.
But Wait! There is an important situation here!
The person needs to start the engine before the battery voltage drops too low to start the car (assuming 11.9V is the critical threshold), we need to consider the relationship between battery voltage, state of charge, and discharge rate.
To maintain the battery voltage above the critical level of 11.9V, and ensure the engine can be started, a person should start the engine before approximately 2.21 hours of using the headlights and interior lighting. This calculation is based on a conservative estimate, aiming to keep the battery discharge above 50% of its capacity to avoid dropping below the critical starting voltage.
Keep in mind, this is a rough estimate and actual results can vary based on factors like the battery’s age, health, and the exact power consumption of the lights.
FAQ 4- How Long Does a Car Battery Last in Accessory Mode?
If the battery is new, its capacity to hold a charge and power accessories in accessory mode will be at its peak, generally around 48 amp-hours for a typical car battery. The duration it can last in this mode will still depend on the specific accessories being used and their power consumption, but here are some more precise estimates considering the battery’s optimal condition:
- Low Consumption (e.g., radio or interior lights only): With minimal use of accessories, consumption can be around 2-5 amps. In this scenario, a new battery could potentially last 9 to 24 hours or more depending on full consumption. [However, to start the engine, it is necessary to prevent the battery discharge from falling below 50% capacity. Battery Voltage should not fall below 11.9V.]
- Moderate Consumption (e.g., infotainment system, some charging devices): For moderate use, the consumption could be around 5-10 amps. This would lead to a battery life in accessory mode of roughly 4.8 to 9.6 hours. [However, to start the engine, it is necessary to prevent the battery discharge from falling below 50% capacity. Battery Voltage should not fall below 11.9V.]
- High Consumption (e.g., multiple accessories including high-end audio systems, and multiple charging devices): If the consumption reaches around 10-15 amps, the battery might last approximately 3.2 to 4.8 hours. [However, to start the engine, it is necessary to prevent the battery discharge from falling below 50% capacity. Battery Voltage should not fall below 11.9V.]
These estimates assume the battery is in optimal condition and fully charged. Despite the new battery’s capacity, it’s crucial to be mindful of how long the car is left in accessory mode to avoid draining the battery. Regularly starting the engine and allowing it to run will help recharge the battery, ensuring it remains ready to start the vehicle when needed.
FAQ 5- How Long Does a Car Battery Last with Ignition On?
When the ignition is on but the engine isn’t running, the car battery powers the ignition system, fuel system, and other electronic accessories and sensors necessary to keep the vehicle in a ready-to-start state. This mode typically consumes more power than accessory mode because it involves more systems, but less than when the engine is running. The actual duration a car battery can last in this state depends significantly on the vehicle’s design, the condition of the battery, and what features are being powered. However, we can make some general estimates:
- Battery Capacity: Assuming a standard car battery with a capacity of about 48 amp-hours.
- Power Consumption: The ignition on mode can consume around 10-20 amps, depending on the vehicle and the electronics in use. This is a rough estimate and can vary.
Given these parameters, a new and fully charged car battery might last between 2.4 to 4.8 hours with the ignition on and the engine off. “However, to start the engine, it is necessary to prevent the battery discharge from falling below 50% capacity. Battery Voltage should not fall below 11.9V.” This is a broad estimation and actual durations will vary based on specific vehicle demands and battery conditions.
Accessory Mode vs. Ignition On Mode: Understanding the Impact on Your Car Battery
Accessory mode and ignition on mode are two different states of a vehicle’s electrical system, each serving different purposes and impacting the car battery in distinct ways. Understanding the differences between these modes can help manage battery health and prevent unnecessary drain.
Accessory Mode (ACC)
- Purpose: Allows the use of electrical accessories like the radio, interior lights, and power windows without running the engine. This mode is typically used for short durations, like listening to music while parked.
- Power Consumption: Generally lower than in ignition-on mode, as fewer systems are powered. Only the accessories deemed necessary without the engine running are active.
- Battery Impact: This can drain the battery over time, but usually at a slower rate compared to ignition-on mode. If the battery is healthy, it might sustain several hours of use in accessory mode without significant drain.
- Typical Use: Waiting in the car, using the radio or charging devices without the need for the engine.
Ignition On Mode
- Purpose: Engages more of the vehicle’s systems than accessory mode, preparing the car to start. This includes the fuel system, ignition system, and various sensors and electronics necessary for the engine to operate.
- Power Consumption: Higher than accessory mode because it powers more systems, even though the engine is not running. The exact consumption depends on the vehicle but is significantly higher due to the readiness of more electrical components.
- Battery Impact: Drains the battery faster than accessory mode due to the higher power demand. A new battery may only last a few hours in this state before needing a recharge.
- Typical Use: The moments before starting the engine or troubleshooting engine problems without actual engine operation.
Key Differences
- Systems Powered: Accessory mode powers only basic electrical accessories, while ignition on mode powers those plus additional systems required for the engine to start.
- Battery Drain Rate: Ignition-on mode generally results in a faster drain on the battery compared to accessory mode due to the increased number of systems being powered.
- Intended Use: The accessory mode is designed for the use of certain features without engine power, ideal for short-term comfort or convenience. Ignition on mode is intended as a transitional state before the engine starts, not for prolonged use due to its higher energy consumption.
In summary, while both modes draw power from the battery without the engine running, ignition on mode engages more of the vehicle’s systems and thus drains the battery more quickly. Understanding these modes helps in making informed decisions about vehicle use to maintain battery health.
FAQ 6- How Long Does a Car Battery Last Without an Alternator?
A car battery’s duration without an alternator functioning properly can vary widely based on several factors, such as the battery’s age and condition, the power demands of the vehicle’s electrical systems, and how the vehicle is being used. The alternator is crucial for charging the battery while the engine runs, so without it, the battery relies solely on its stored charge to power everything.
Key Factors Influencing Battery Life Without an Alternator:
- Battery Capacity: Most car batteries have a capacity of about 48 amp-hours (Ah).
- Vehicle’s Electrical Load: The number of electrical systems in use (headlights, radio, air conditioning, etc.) significantly affects how quickly the battery will drain.
- Battery Condition: A new, fully charged battery will last longer than one that’s older or not fully charged.
General Estimate:
- Minimal Electrical Usage: With minimal use of electrical components (e.g., no headlights, AC, and minimal use of the radio), a new and fully charged battery might power a car’s essential functions (ignition, fuel pumps, basic electronics) for several hours before running out. This is under ideal conditions and assumes very conservative use of electrical accessories.
- Typical Electrical Usage: For normal or typical use, including headlights and other essential electronics, the battery might last anywhere from 20 minutes to a couple of hours.
It’s important to note that running a car without an alternator is not sustainable. The battery will eventually drain completely, leaving the vehicle unable to start or operate. Furthermore, attempting to drive under these conditions can be dangerous, as critical systems like power steering and brakes may become less effective as the battery voltage drops.
If you suspect your alternator is failing or has failed, it’s advisable to address the issue as soon as possible to avoid being stranded and to prevent potential damage to the electrical system or battery from deep discharging.
FAQ 7- How Long Does a Car Battery Last on an Inverter?
The duration a car battery will last when powering an inverter depends on the battery’s capacity, the power demand of the devices being powered by the inverter, and the efficiency of the inverter itself. Inverters convert the DC power from the battery to AC power for household devices, and this process is not 100% efficient, usually around 85-90% for good quality inverters.
Key Factors:
- Battery Capacity: Measured in amp-hours (Ah), indicating how much current a battery can supply over time. For example, a typical car battery might have a capacity of about 48 Ah.
- Power Demand: The total wattage of the devices being powered. For example, if you’re powering a 100W laptop, the inverter needs to draw about 100W from the battery.
- Inverter Efficiency: Assuming an efficiency of about 85%, more power than the device rating is drawn from the battery to account for energy loss during conversion.
Calculation:
To estimate how long a battery would last, you can use the formula:
Battery Life (hours)=[Battery Capacity (Ah)×Battery Voltage (V)×Inverter Efficiency](÷) Power Demand (W)
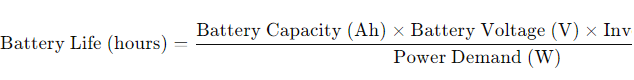
Assuming a 12V battery system, a 48 Ah battery, an inverter efficiency of 85% (0.85), and power demand of 100W let’s calculate the approximate duration.
Let’s perform this calculation to give you a clearer idea.
Using a 48 Ah car battery at 12V to power a 100W device through an inverter with 85% efficiency, the battery would last approximately 4.9 hours. [However, to start the engine, it is necessary to prevent the battery discharge from falling below 50% capacity. Battery Voltage should not fall below 11.9V.] This is an estimate, and actual performance can vary based on specific conditions, including the battery’s age and health, the exact efficiency of the inverter, and the power demand variability of the connected devices.
FAQ 8- How Long Does a Car Battery Last on a Shelf / in a Storage?
A recharged or new car battery’s shelf life—how long it can sit unused before it starts losing significant charge—varies depending on a few factors, such as the type of battery, and storage conditions.
- Storage Conditions: The ideal storage condition for a car battery is in a cool, dry place. High temperatures accelerate the self-discharge rate and can lead to sulfation(only for lead-acid batteries), which damages the battery.
- Shelf Life: A new, fully charged lead-acid car battery stored under ideal conditions might last from 6 months to over a year before its charge drops significantly. However, it’s recommended to periodically check the battery voltage and charge it if it drops below 12.4 volts to maintain its health. AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries, have lower self-discharge rates compared to traditional flooded lead-acid batteries and can sit unused for longer without significant charge loss.
- Maintenance: To extend the shelf life, it’s beneficial to store the battery with a trickle charger or a battery maintainer attached. These devices provide a small, steady charge to counteract the natural self-discharge rate.
Best Practices:
- Check the battery voltage every 3 to 6 months and recharge if necessary to prevent deep discharge.
- Avoid storing batteries on concrete floors for extended periods, as temperature fluctuations can cause condensation and accelerate discharge (though this is less of a concern with modern battery cases).
[To start the engine, it is necessary to prevent the battery discharge from falling below 50% capacity. Battery Voltage should not fall below 11.9V.]
In summary, a new or recharged car battery can last on a shelf for 6 months to a year or more, depending on storage conditions and battery maintenance. Periodic checks and maintenance charging are key to preserving battery life during storage.
FAQ 9- How Long Does a Car Battery Last Disconnected?
When a car battery is disconnected, it’s isolated from the vehicle’s electrical system, which prevents the battery from being drained by any parasitic loads (small electrical loads that continue even when the car is off, like clock or security system). However, even a disconnected battery will self-discharge over time. The rate of self-discharge depends on the battery type and the storage conditions. Here are some considerations:
Self-Discharge Rate: Lead-acid batteries, including AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) and gel types, have a self-discharge rate of about 4% per month under ideal storage conditions.
Storage Conditions: The environment in which the battery is stored significantly impacts its discharge rate. Cooler temperatures slow down the self-discharge process, while high temperatures accelerate it.
Shelf Life When Disconnected: Under optimal conditions (cool, dry, and away from extreme temperatures), a disconnected lead-acid car battery might retain a charge for 6 months to a year before it needs recharging. However, it’s recommended to check the battery’s charge every 3 to 6 months and top it off as needed to avoid deep discharge.
FAQ 10- How Long Does a Car Battery Last Without Driving / Engine Off?
- New Battery: A new, healthy car battery, fully charged, might last anywhere from 2 to 3 months without driving under optimal conditions. This period can be shorter in extreme weather conditions or if the car has systems that draw more power when parked.
- Older Battery: For an older battery or one that’s not in optimal condition, the period it can last without driving might be significantly shorter, potentially only a few weeks.
FAQ 11- How Long Does a Car Battery Last on the Radio / Listening to Music?
Here’s a rough estimation considering a new or fully recharged typical car battery:
Factors to Consider:
- Battery Capacity: A typical new car battery has a capacity of about 48 amp-hours (Ah).
- Radio Power Consumption: Although the power consumption of car radios can vary, a typical car radio might consume between 5 to 10 watts when in use.
Given these parameters, we can make a rough estimate. Since the radio’s power consumption is relatively low, the primary factor is the battery’s capacity and the efficiency of the system.
To convert the radio’s power consumption into current drawn from the battery, we use the formula: I=V÷P, where I is the current in amperes, P is the power in watts, and V is the voltage of the battery (usually about 12 volts for a car battery).
Assuming a consumption of 10 watts for easier calculation and a 12V system, the current draw would be approximately,
10A÷12A=0.8310
10W÷12V=0.83 amperes hour (or 830 milliamperes).
Using the battery capacity, we can estimate how long the battery could last:
48Ah ÷0.83A≈57.83 hours in theory.
[However, to start the engine, it is necessary to prevent the battery discharge from falling below 50% capacity. Battery Voltage should not fall below 11.9V.]
Practical Considerations:
- This is a simplified calculation assuming optimal conditions. Real-world factors can reduce this duration.
- Other electrical draws (like interior lights or charging devices) will decrease battery life.
- Battery health: Even if new or recharged, actual performance can vary slightly based on specific battery conditions and environmental factors.
Under ideal conditions, a new or fully recharged typical car battery could theoretically power a car radio for well over two days continuously without running the engine or using other significant electrical accessories. However, to avoid draining your car battery unnecessarily, it’s prudent not to use the radio for extended periods without starting the engine periodically to recharge the battery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the lifespan of a car battery under various conditions is a topic of great importance for vehicle owners. From how long a battery lasts after being charged or jump-started, to its endurance when powering accessories like lights, the radio, or an inverter, each scenario presents its own set of factors that can affect battery life. Understanding these nuances can help motorists manage their battery’s health more effectively, ensuring reliability and extending the battery’s service life.
We’ve explored how environmental conditions, battery age, and usage patterns influence battery performance in different states – whether in accessory mode, without an alternator, or when disconnected. The key takeaway is the importance of regular maintenance and mindful usage. For instance, minimizing unnecessary drain, like limiting the use of electronics when the engine is off, and keeping the battery charged, either by regular driving or using a maintainer, can significantly impact the battery’s longevity.
Additionally, knowing the potential drain sources, such as the use of air conditioning, lights, or entertainment systems, allows for better planning and battery management. For batteries in storage or those that are disconnected, understanding the self-discharge rate and the benefits of proper storage conditions can prevent unexpected depletion.
Ultimately, the goal of this post is to empower vehicle owners with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding their car batteries. By recognizing the factors that affect battery life in various scenarios, you can take proactive steps to maintain your battery’s health, ensuring that your vehicle is always ready when you need it. Remember, the longevity of a car battery is not just about the battery itself but how it is used and cared for.
Please note that this post contains affiliate links. This means if you click on a link and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. Our reviews and recommendations are based on our own opinions and analysis, and we aim to provide you with the most accurate and helpful information to make your decisions. Your support helps us continue to provide valuable content. Thank you for your understanding and support.









